LESSON 4
4.1 DENTITION
This refers to the number, arrangement and shape of teeth in an animal.
In mammals, two sets of teeth occur in one’s life time i.e. the milk teeth and permanent teeth. The first set is called the milk teeth which arises when the animal is young and lasts for relatively a short time. Milk teeth in man are 20 in number and normally get replaced by permanent teeth at the age of usually 7 to 11 years.
4.2 DENTAL FORMULA
This is a formula indicating the number of each type of teeth in half the upper jaw and half the lower jaw. The dental formula gives evidence that the dentition of an animal is closely related to its diet. The number of teeth in the upper jaw is written above that of the lower jaw. The different types of teeth are represented by letters i.e.
Incisors (i)
Canines (c)
Molars (m)
Premolars (pm)
4.3 Dental formulae of some animals
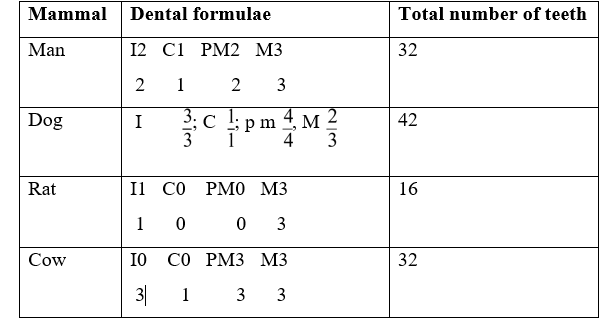
E.g. the dental formula of an adult human is written as below:
I ; C ; p m , M = 32
This means that man has 2 incisors on each half on the top and lower jaws, one canine on each half of the top and lower jaws, 2 premolars on each half of the top and lower jaws. Therefore man has 8 teeth on each half on the jaws which adds up a total of 32 teeth.
Although hard teeth are delicate and need proper care if their life is to be sustained. Common problems that may arise if teeth are not cared for include:-
i) Tooth decay or dental caries.
This is caused by lodging (when food gets stuck) of food particles especially sugars between the teeth. This food is then attacked by micro-organisms (bacteria) which ferment this food producing an acid which reacts chemically with the enamel and removes calcium from it making it soft. During chewing, the soft part of the enamel begins wearing away forming a hole which gets larger and larger as more food gets stuck in the now bigger hole and fermentation process continues. Tooth ache commences into the dentine, the pulp cavity with nerves and blood vessels get affected and a lot of pain is felt.
ii) Periodental diseases.
These are diseases which make the gum soft and flabby so that they do not support the tooth well. Sometimes these diseases may lead to bleeding of the gum and passing out of pus. The 2 periodental diseases known are;
- Pyorrhea
- Gingivitis
They are characterized by reddening of the gums, bleeding and presences of pus in the gums.
4.5 Prevention of dental decay and proper care of teeth
- Visit a dentist regularly for checkup.
- Proper cleaning of teeth (brushing after meals)
- Avoid sweet sugary foods like sweets which encourage bacterial growth.
- Avoid opening bottles using teeth carrying desks.
- Avoid eating very hot and very cold foods especially at a go since they result into alternate expansion and contraction since it leads to cracking or chipping of the enamel.
- Eating foods rich in calcium, phosphates and vitamins A, D, and C
- Exercising your teeth by eating hard fibrous foods like sugar canes, carrots, etc. This stimulates the flow of saliva which neutralizes acids formed bacterial fermentation.