LESSON ONE
FORMULAE AND EQUATIONS
Chemical formulae: The chemical formula of a compound consists of symbols of the elements and numbers to show the ratio in which the different atoms are present. E.g. carbon dioxide has the formula, CO2. This means it contains one carbon atom for every two oxygen atoms. The ratio of atoms within a chemical compound is usually constant.
NB: The formula of an element or compound is the symbols and numbers which mean one molecule. Molecules: A molecule is the smallest particle of an element or compound which can normally exist on its own. Substances such as water and gases consist of molecules. Some substances contain atoms of the same elements while others consist of atoms of different elements chemically combined together.
Atomicity is the number of atoms in one molecule of the element.
Types of molecules
1. Diatomic molecules – this consist of two atoms of the same element.
Examples:
H2 – Hydrogen molecule
O2 – Oxygen molecule
Cl2 – Chlorine molecule
N2 – Nitrogen molecules
2. Tri-atomic molecules – This consist of three atoms of the same element e.g Ozone ( O3)
3. Tetra- atomic molecules – This consist of four atoms of the same element e.g P4
4. Polyatomic molecules – This consist of many atoms of the same element e.g S8
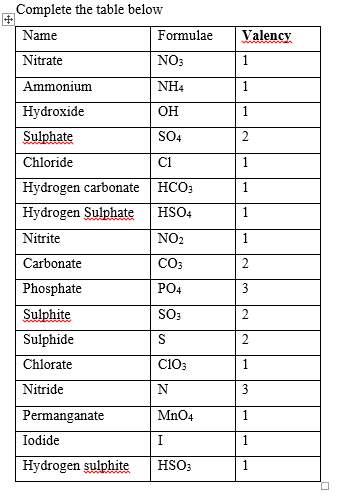
VALENCY: This is the power of an element or radical to combine with others. The valency of an element or radial is the number of hydrogen atoms that it will combine with or that it will displace from an acid. The size of charge on an ion is valency.
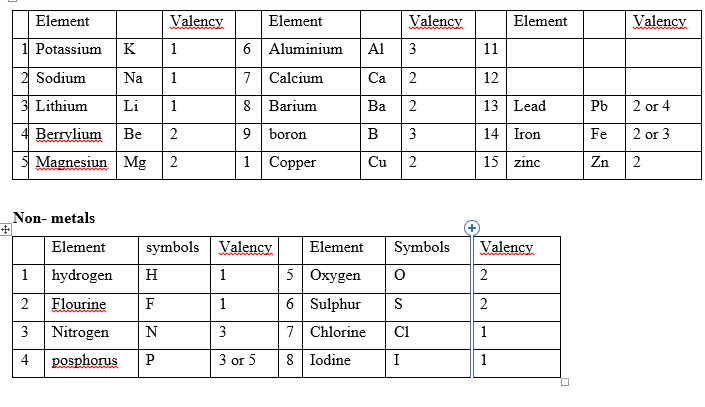
VALENCIES OF ELEMENTS
Metals
RADICALS: A radical is a group of atoms that exist in several compounds but does not exist on its own. They are a group of atoms that carry a charge. Radicals may be negatively or positively charged ions.