LESSON 5
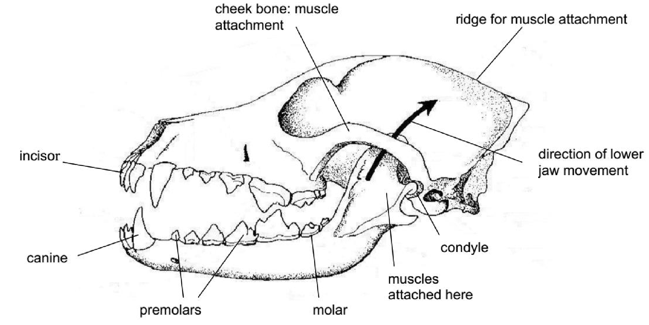
5.1 CARNIVORE DENTITION
Carnivorous animals such as dogs, cats and lions are adapted for feeding on other animals.
Their teeth are adapted for capturing and killing other animals and tearing their flesh.
Their incisors are chisel shaped and enable them to grip and strip off pieces of flesh from bones.
Their canines are long, curved and pointed used for piercing the prey and preventing it from escaping.
The upper fourth premolar and the first lower molar are large and powerful. They are called carnassial teeth. They overlap like blades of scissors and are used for tearing and slicing flesh.
The other premolars and molars have jagged edges that fit perfectly together making them ideal for cracking bones.
5.2 Diagram showing dentition in the carnivore e.g. a dog
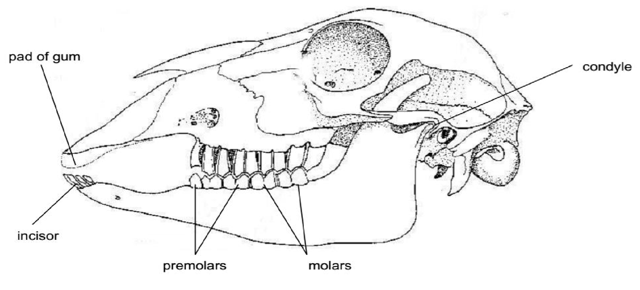
5.3 HERBIVORE DENTITION
Herbivorous animals e.g. cows, goats and elephants eat plant foods such as grass, leaves and small stems.
Their teeth are adapted for crushing and grinding vegetables.
Their incisors and canines are chisel shaped and only found in the lower jaw.
In the upper jaw, the incisors and canines are replaced by a thick horny pad. Grass and other vegetation are gripped between the incisors and canines on the lower jaw and the horny pad.
Between the front teeth and the cheek teeth is a large gap called diastema. It provides space for the tongue to manipulate vegetation in such a way that the material being chewed is kept away from that which is freshly gathered.
5.4 Dentition of a sheep
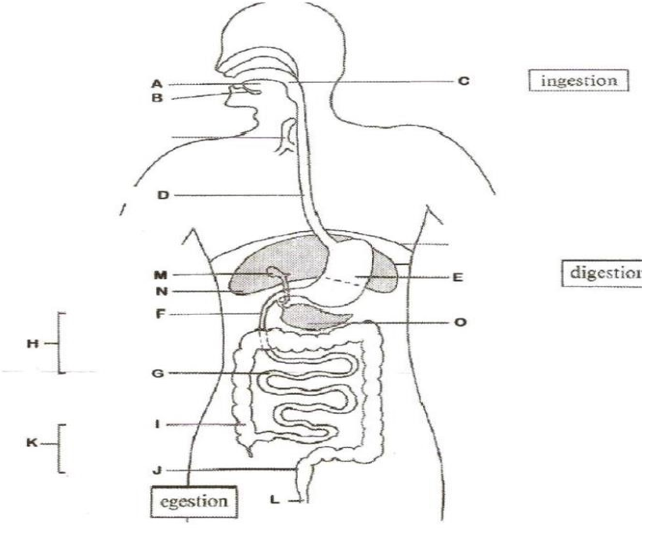
5.5 DIGESTION IN MAN
Digestion is the process by which complex food substances are broken down into simpler soluble compounds that can be absorbed and assimilated (utilized) by the body.
Digestion can be divided into; physical or mechanical digestion and chemical digestion.
Physical digestion:
This is the breakdown of food due to the mechanical action of teeth, muscular contractions and bile juice.
Chemical digestion: This is the breakdown of food due to enzyme action or enzymatic action.
5.6 Extracellular digestion:
When digestion occurs or takes place outside the body or cells, it is called extracellular digestion. This may not necessarily be outside the body but it may occur inside the body but not inside cells. E.g. in fungi, man etc.
Intracellular digestion: This is a type of digestion which take place inside the body cells eg Amoeba, Paramecium.
Note: digestion in man is extracellular digestion because the enzymes are released in the gut cavity where digestion occurs.
5.7 Steps involved in digestion of food
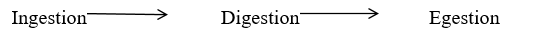
Ingestion
Is the taking in of food into the body
Egestion
This is the process by which insoluble undigested compounds of food are discharged or expelled from the body as faeces.
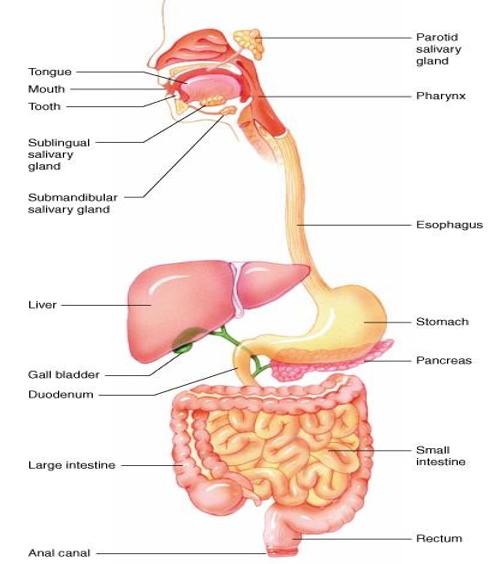
The human alimentary canal