LESSON 8
8.1 DIGESTION IN THE ILEUM
This is where final digestion takes place.
Food moves down from the duodenum into the ileum by peristalsis.
The presence of food in the ileum stimulates the secretion of the intestinal juice, succus entericus by walls of the ileum.
Succus entericus contains several enzymes which complete the process of digestion forming a milky fluid substance called chyle (food after final digestion is called chyle).
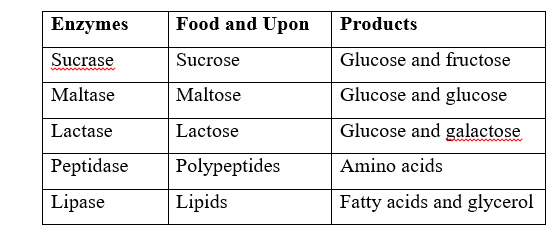
The composition of chyle is a group of soluble end products of digestion namely; Glucose, Fructose, Amino acids, Glycerol, Vitamins and Mineral salts.
8.2 DIGESTION IN THE LARGE INTESTINES / COLON
In the colon, water and mineral salts are absorbed. The undigested and indigestible food substances pass down into the large intestines which are eventually removed from the body as faeces through the anus. There is no digestion in the large intestine.
Accumulation of hard particles like stones, small sticks in the appendix results into a condition known as appendicitis. The appendix is thus removed surgically by a simple operation.
8.3 SAMPLE QUESTIONS:
Question 1: Describe the digestion process that occurs when a person consumes Posho (starch)?
Answer:
A piece of Posho is placed into the mouth, a process called ingestion.
In the mouth; The Posho is thoroughly chewed by teeth, breaking it into smaller particles. During this chewing, Posho is mixed with saliva to make it soft and easy to swallow.
Saliva contains salivary amylase which breaks down cooked starch in Posho into maltose under neutral conditions.
Food is then pushed down the Oesophagus by a process called peristalysis. In the stomach; no digestion of starch occurs because of acidic conditions due to presence of hydrochloric acid which provide unfavourable pH for activity of salivary amylase.
In the duodenum; the pancreatic juice contains pancreatic amylase which speeds up the breakdown of undigested cooked starch to maltose.
In the ileum, intestinal juice contains maltase which speed up the breakdown of maltose to glucose molecules which are soluble hence easily absorbed by the body.
This marks the end of the digestion for Posho.
Question 2:
Describe the process of digestion of proteins in man.
Answer:
In the mouth; Protein food is chewed by the teeth and swallowed into the stomach. In the stomach; gastric juice is produced which contain pepsin that digests proteins to peptides and rennin coagulates protein milk in babies.
In the duodenum; presence of food stimulates pancreas to secrete pancreatic juice containing trypsin which digests undigested proteins to peptides.
In the ileum; intestinal juice is produced containing peptidase which break down peptides to amino acids which are later absorbed through the ileum walls.
8.4 THE PROCESS OF ABSORPTION AND ASSIMILATION OF FOOD ABSORPTION
Absorption is the process by which soluble products of digestion diffuse through the cellular lining of the villi into the blood stream.
The villi are located in the ileum (small intestine) and thus absorption takes place in the small intestine. Some nutrients like minerals and vitamins also enter the villi by active transport.
The ileum shows various adaptions to suit the process of absorption which includes:
- It is highly coiled/folded and consequently long thus providing a large surface area for digestion and absorption of food. (It is six (6) meters long).
- Has a thin layer of cells to reduce the diffusion distance over which soluble food passes through.
- They are highly supplied with blood capillaries and lacteals which transport away absorbed food thus maintaining a diffusion gradient. iv) Have figure-like projections called the villi which increase the surface area for absorption of soluble food.
- The villi also have hair like extensions called the micro villi whichs further increase the surface area for absorption of soluble food products. The villi are the actual sites for absorption of soluble food products.
8.5 Diagram of Villus
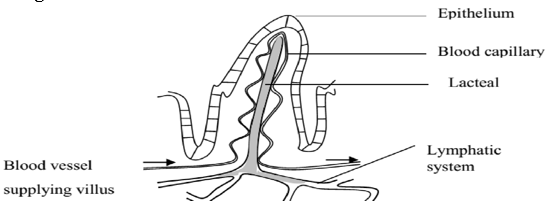
Fatty acids and glycerol are absorbed into the lacteal of the villi. These lacteal later join up to form the lymphatic system carrying these food materials and distributing them to all parts of the body.
Glucose, Amino acids and Fructose pass into the blood capillaries of the villus which join up to form the Hepatic portal vein which transport these nutrients to the liver.