LESSON 1
1.1 Introduction
Production refers to an economic activity that aims at transforming raw materials into finished consumable products (goods and services).
OR production refers to the process of creating utility in goods and services in order to satisfy human wants.
1.2 Purpose of production
- To satisfy individual desires and needs of other people (human wants)
- To increase the economic welfare of the people (standard of living).
- To create employment opportunities in the economy
- To utilize the existing resources such as land
- To utilize the existing infrastructure
- To attain a given political objective
1.3 Categories of production
- Primary production
This involves production of raw materials or extraction of raw materials from natural resources such as farming, mining, fishing etc
- Secondary production
This involves the process of transforming raw materials into finished consumable products such as food processing, carpentry, construction, manufacturing etc
- Tertiary production
This is the production of services such as banking, ware housing, advertising, transportation, insurance, services by doctors, teachers etc. The services produced are both commercial and direct.
1.4 Direct and indirect production
Direct production is the production of goods and services for producer’s own consumption. It is sometimes called subsistence production.
While
Indirect production is the production of goods and services for exchange with other people /for market.
Note:
Production as a process of creating wealth—production involves making economic goods and services which form the real wealth of individuals or nations. A wealth nation or individual therefore is one with a lot of economic goods and services.
1.5 Factors of production (Agents of production)
These are the resources that are employed in the production of goods and services so as to satisfy human wants.
The factors of production include:
- Land
- Labour
- Capital
- Entrepreneurship
1.6 LAND
Refers to all gifts of nature on, under, and above the earth’s surface such as soils, vegetation, water, climate, etc
1.7 Characteristics of land
- The supply of land is fixed (it experiences a perfectly elastic supply curve)
- It is a free gift of nature
- It is geographically immobile but can be occupationally mobile.
- Payment to land is called rent
- Its productivity can be changed using units of other factors especially labour and capital.
1.8 Uses of land
- Land is used for agricultural production
- It is a source of raw materials.
- Provides space where production can take place.
- It is a source of food such as water, fish etc
- Used to establish recreational facilities such as beaches, football grounds etc
1.9 Payment to land
The payment to land is rent–economic rent.
Economic rent refers to the payment / reward to a factor of production over and above its supply price.
A Supply price/ transfer earnings refers to the minimum reward to a factor of production in order to keep it in its present occupation.
1.10 Reasons why the payment to land is economic rent
The supply of land is fixed / perfectly inelastic.
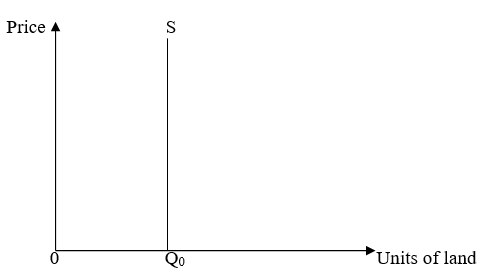
Amount of land OQ0 is available not only at price p1 but at any price whether p2 or p3 even at 0 price.
Land is a free gift of nature with no supply price. Economic rent depends on the elasticity of supply. The more inelastic the supply of the factor, the greater the amount of the economic rent and the more elastic the supply of the factor, the smaller the amount of economic rent.
